本文共 11715 字,大约阅读时间需要 39 分钟。
Since 2011, Alibaba Group has been actively involved in building open source communities, with the number of open source projects increasing every year. Currently, Alibaba has 150+ open source projects, each with over 10,000 GitHub stars!
GitHub statistics from 2017 show that Alibaba is the only Chinese company to be included in GitHub's top contributor list. Furthermore, Alibaba is ranked number 5 in the Top 20 Most Popular Chinese OSS survey conducted by OSChina.
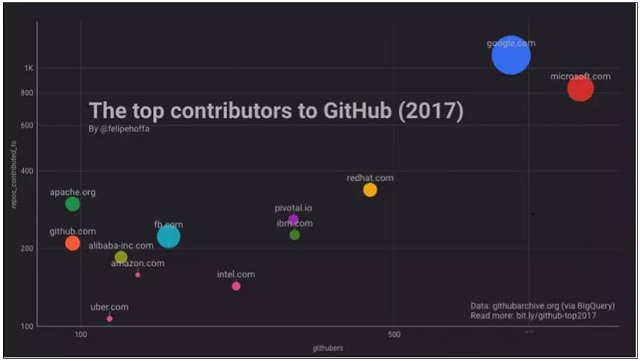
In reality, Alibaba employees do not get rewarded for open source projects. All teams have voluntarily contributed to various open source projects, including sharing their experiences or helping others to solve problems. This is exactly what the spirit of open source development is. It’s where everyone can build on each other's knowledge, and everyone is both a teacher and a student.
We have already witnessed the paradigm shift from mainframes to distributed systems. Mainframes are simple to deploy and do not need multi-node configuration, but, on the other hand, they are expensive, hard to maintain and have a single point of failure. A distributed system composed of smaller servers costs less, and, at the same time, makes the entire system more concurrent, expandable and reliable.
1. Dubbo – Major Upgrade of the Distributed RPC Framework
Dubbo is a high performance RPC framework in Java. It has been open source since as early as 2012 and has been in favor among Chinese open source enthusiasts and the industry for years. Though it has been maintained constantly, the daily maintenance cannot fulfill the demands of this enormous community. As Alibaba grows—while still making sure the service to the company and our customers is priority number one—we can allocate more resources to these open source projects that services the whole of society.
This year, Dubbo's development got restarted and major upgrades were made. Dubbo2's design principles emphasize scalability, light weight, and adaptability to open source peripherals and protocols. It not only fixes some of the framework defects such as elegant downtime and annotated configuration but also adds a communication module and thread stack along with greatly improved stability.
Let's look at some details. Dubbo published five versions this year, 2.5.4, 2.5.5, 2.5.6, 2.5.7 and 2.5.8. It fixed and merged the most commented upon issues and Pull Requests, and it also made the following improvements: Netty4 support, annotation, Java 8 support, and Docker support. Dubbo will continue improving itself for the perceivable future. New projects include Dubbo Spring Boot Starter, RESTful support, graceful deployment, error tolerance improvement, routing policy improvement and async improvements.
Other than the framework itself, the Dubbo team also launched a new website (with over 3500 daily views) and updated their documentation. In order to spread its influence, the team translated their website, documentation and code into English. This has already begun to produce some visible effects. The noted technical blog baeldung published an article “Introduction to Dubbo” which gave an in-depth introduction to Dubbo. The team participated in interviews by OSChina and InfoQ. It is on the OSC Top 20 most popular open source software of 2017.
Dubbo made major upgrades because of the observed trends in technology that are particularly relevant to RPC. The future will focus on Cloud Native, multi-language enhancements, microservices support and more. Dubbo will continue to build its ecosystem and community as well as building international influence.
We welcome you to discuss with the Dubbo development team:
2. RocketMQ – The Distributed Message Middleware
The Apache Software Foundation announced on Sept 9 that the open-source project RocketMQ—donated by Alibaba Cloud to the Apache Incubator—has graduated from the Apache Incubator to become a Top-Level Project (TLP), signifying that Apache RocketMQ henceforth becomes the first non-Hadoop Apache TLP among all Internet middleware in China. This year, RocketMQ has won the 12th China Japan Korea OSS award and was on OSChina’s 2017 Top 20 most popular Chinese open source software list.
RocketMQ is Alibaba Cloud’s third-generation distributed messaging middleware. It was announced as open source in 2012. The MQ for business is available on Alibaba Cloud. RocketMQ undertook all message transmissions of Alibaba Cloud production systems during the November 11th Single's Day shopping festival. Last year, on November 11th, RocketMQ delivered 1.2 trillion messages with precision and low latency, with the peak traffic hitting 170,000 transactions/second.
RocketMQ originated in China, but it already has attracted worldwide attention. RocketMQ won the 2015 China Japan Korea OSS award, and it has entered the mainstream open source sites around the world. Over 100 companies and research institutes are currently using RocketMQ. It is worth mentioning that the United States is the second most region visiting the RocketMQ project site.
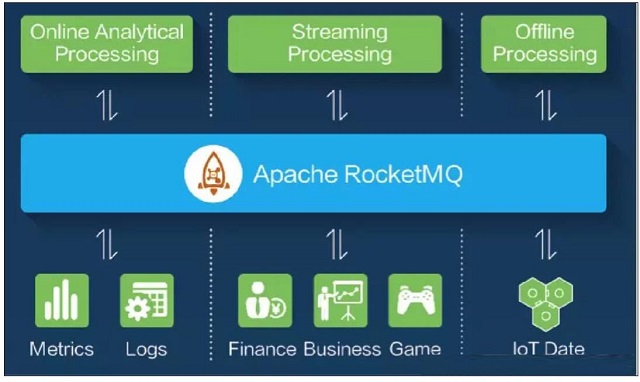
As a distributed messaging engine, RocketMQ features include:
- Low latency and high concurrency. More than 99.6% response latency within 1 millisecond.
- Finance-oriented. High availability with tracking and auditing features.
- Industry-sustainable. Trillion-level message capacity guaranteed.
- Vendor-neutral. Support multiple messaging protocols like JMS and OpenMessaging.
- Reliable performance. Accumulate messages without performance loss given sufficient disk space.
Related:
3. Fastjson – Database Connection Pool Druid and JSON Parsing Library
Druid is the only database connection pool used by Alibaba. it supports some of the most critical scenarios such as the ones faced on Single's Day. Druid has a slogan: “monitoring the connection pool for the sake of monitoring.” After six years of open source development, Druid has been increasingly mature and is gaining reputation. It is becoming the key technology among many teams.
Fastjson is widely used in both server and client side Android. Almost every Java application from Alibaba has used fastjson.
This is a high performance and complete JSON library. It raised JSON parsing performance to the maximum through the "assumed ordered fast matching" algorithm. It is said to be the fastest JSON library in Java. The Fastjson API is easy to use, and it has been widely used in buffer ordering, protocol exchanges, web output and client-side Android.
Compared to others, these two relatively mature projects did not change much this year. Every month there's a minor version change from the feedback loop of issues. In the future, Druid will increase its monitoring ability and its integration with other Alibaba cloud services. The parser module will become its own independent project.
Related:
4. ApsaraCache for Redis
ApsaraCache is a fork of Redis (the cloud database). It is a branch that started to be maintained on the basis of Redis version 2.8 and backported some features found in 3.0 branches. This version mainly solves the problems of users in the cloud who are concerned about stability, performance, recovery and smooth upgrade experience.
Before ApsaraCache went open source, this solution had many successful cases of application. It has customers in live video (miaopai.com, yizhibo.com, inke.cn, and cctv.com), the gaming industry (immomo.com, Dragonest, Longtu Game, and ChangYou), the news industry (toutiao.com), traffic (amap.com), and finance (Ant Financial). Its application covers an extensive variety of user cases.
There have been many successful use cases of ApsaraCache. Why does it need to be made open source? The reasons are as follows:
- The userbase and usage pattern of Redis in China has changed profoundly. Redis follows a minimalist philosophy of design and stability. In some scenarios, the stability and performance of Redis are subject to new challenges. In addition, many customers on the cloud using Redis have encountered a variety of problems. Based on these problems and challenges, ApsaraCache reconstructed and transformed Redis. In order to empower Redis users, and also for Redis development enthusiasts to better participate, we decided Open ApsaraCache.
- Redis is BSD licensed, featuring a certain degree of freedom. Its latest version Redis 4.0 supports Redis Module which is AGPL licensed. ApsaraCache will support Redis Module later and open source the module code. In this sense, ApsaraCache going open source is also a manifestation of its respect and compliance with the open source protocol.
- ApsaraCache has been waiting for the release of Redis 4.0. After the release, it will actively promote feature fusion of the two sides and strive to merge the features to the major version of the community.
Redis founder Salvatore Sanfilippo (Antirez) held that ApsaraCache going open source is a good thing and can attract more Redis core specialists across the world, which, in turn, will further improve the product stability and availability. He also said that Alibaba Cloud is capable of developing Redis products and hoped to work with Alibaba Cloud together to improve and explore product features.
ApsaraCache was officially made open source in October. The new version will have two more features: it solved the stability bottleneck caused by frequent AOF Rewrite with time-based recovery to precision in seconds; it also solved the syncing problem when there's a patchy connection.
Related:
5. Pouch and Dragonfly – The Rich Container Technology and File Distribution System
Pouch is an internal container tool developed by Alibaba. Currently there are hundreds of thousands of Pouch containers running in the data center, supporting internal online/offline tasks.
First of all, Pouch is a rich container technology which gives a user an experience comparable to virtual machines. It has init process and contains many system services. Secondly, through kernel reinforcement and light-weight virtual machine support, Pouch provides a large security isolation. In terms of mirror distribution, especial those requires massive distribution scenario, it can reduce internet load through p2p. In terms of kernel compatibility, it is comparable to industrial usages, realizing that most IT systems would have outdated kernels.
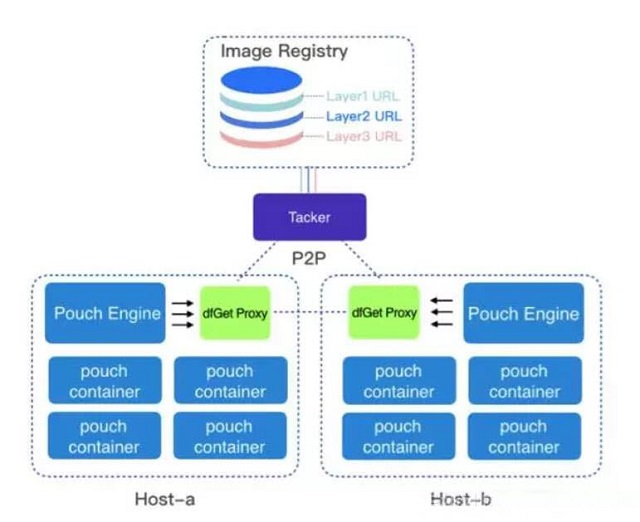
Architectural diagram of Pouch & Dragonfly
The traditional way of download yields two problems. First, when it comes to large files all the retries after failure reduce performances. Second, if client side tries to download everything it could crash the file source.
Dragonfly, on the other hand, uses a p2p method to download files. This effectively reduces the file source pressure. It also supports continuing downloads at the point where it failed. Another feature of Dragonfly is in its integration with Docker and Pouch. It uses a mirror image to preheat. Docker mirror downloads are slow, but through p2p technology Dragonfly has solved this problem.
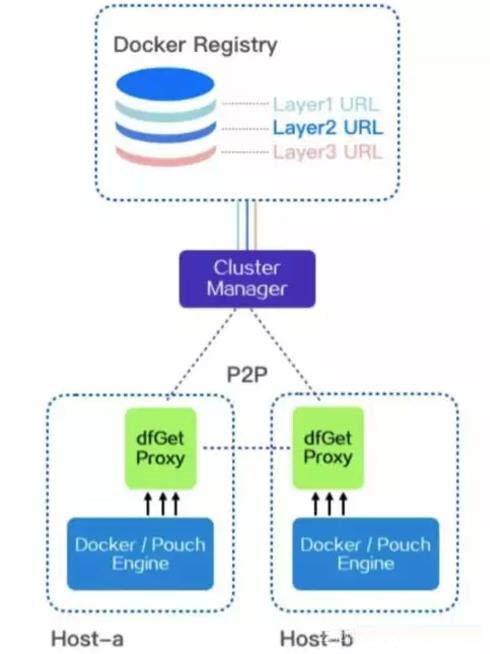
Dragonfly p2p container mirror distribution chart
Dragonfly meets the downloading requirement for Docker and Pouch users’ large downloads (such as big image files). For overseas nodes, Dragonfly can effectively reduce international bandwidth.
There are two versions of Dragonfly: the open source version supports Apache 2.0 protocol, and it can be used in p2p file distribution, container mirror distribution, partial rate limiting and disk volume prediction; the Enterprise version also supports continuation of failed downloads, full rate limiting, mirror preheating, in-memory file system, smart network control, smart dynamic compression and smart routing. The enterprise edition is available in Alibaba's cloud service.
Related:
to continue reading Part 2 of the list!
转载地址:http://tbddx.baihongyu.com/